CS247 Lecture 21
Last Time: D in SOLID, Visitor Pattern
This Time: CRTP, Polymorphic Cloning
I’m still not satisfied with this visitor pattern. Too much code!
There is going to be a lot of methods: If we have subclasses of and subclasses of different methods to write.
Annoying part: Boilerplate - write the following in each DerivedEnemy:
class DerivedEnemy: public Enemy{
public:
void beStruckBy(Weapon& w){
w.strike(*this);
}
};- Must be done for every single
DerivedEnemy - Cannot put it in
Enemy:
class Enemy{
public:
void beStruckBy(Weapon& w){
w.strike(*this); // this is just an Enemy
}
};Doesn’t work - type of *this is wrong. It’s not telling us what the dynamic type is.
Solution to fixing the boilerplate code: CRTP Curiously Recurring Template Pattern
Template our superclass with a type parameter - inherit AND substitute the derived class type.
template<typename T> class Base{
...
};
class Derived: Base<Derived> { // : publicly inheriting. At this point, we know Derived is a class.
... // We can use T in Base as if we have provided a forward declaration
};How do we use this to fix the boilerplate code? ()
template<typename T> class Enemy{
public:
void beStruckBy(Weapon& w){
w.strike(*static_cast<T*>(this));
}
};
class Monster: public Enemy<Monster> {...};
class Turtle: public Enemy<Turtuel> {...};- created a template base class
Enemythat takes the derived class type as a template parameter. - then derive enemy classes from the
Enemytemplate and provide the derived class type as template argument.
This sort of works:
Weapon* w = ... ;
Turtle t{...};
t.beStruckBy(*w); // calls Enemy<Turtle>::beStruckBy- when we call
beStruckByon an enemy instance, the CRTP pattern ensures that the correctw.strikemethod is called on the dynamic type of the enemy.
Cast *this from type Enemy<Turtle>* to Turtle* allows us to override into Rock::Strike(Turtle&) (or stick).
Explanation
Key here is that by using CRTP, the
thispointer static type isEnemy<Turtle>*but its dynamic type isTurtle*. The caststatic_cast<T*>(this)effectively changes the static type toTurtle*, which allows the correctw.strikemethod to be called based on the dynamic type.
Issue: Now, we have different superclasses for each Enemy:
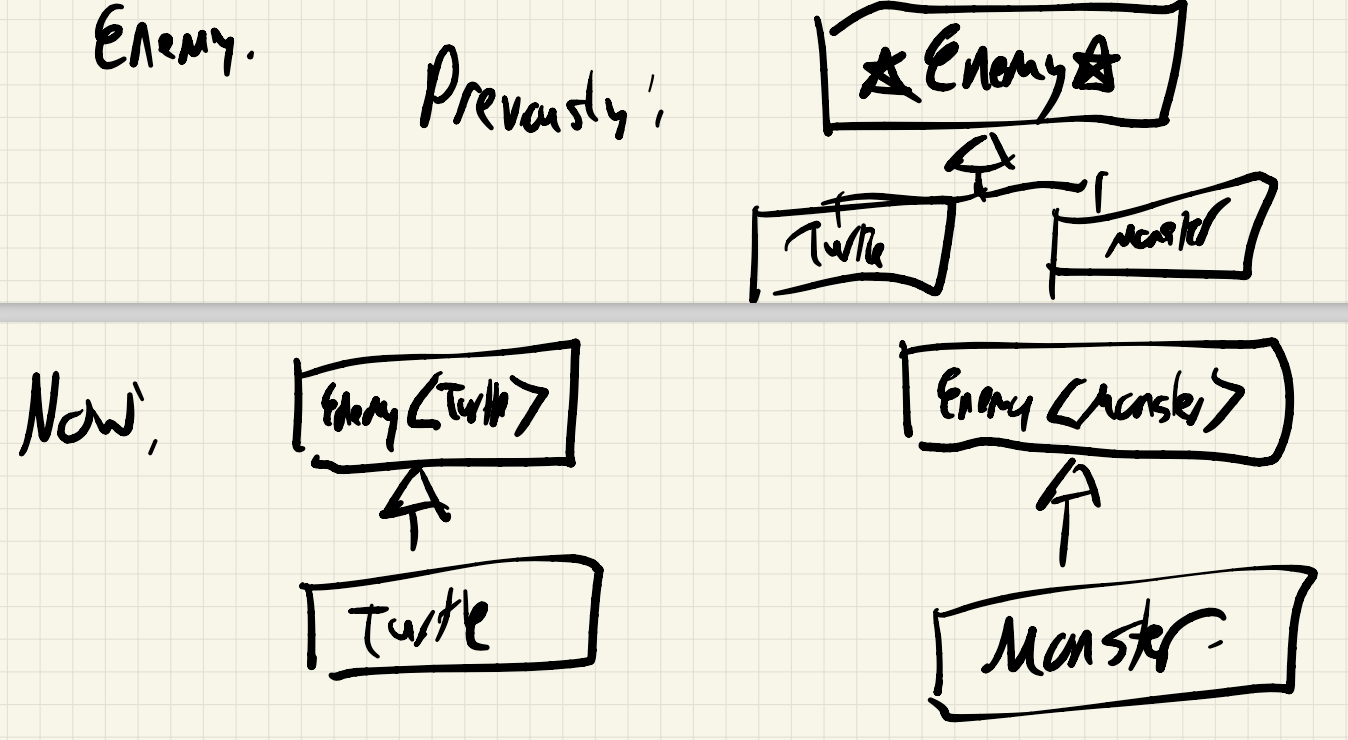
Because Enemy<Turtle> and Enemy<Monster> are different classes, we can no longer use Enemys polymorphically.
- No
vector<Enemy*>allowed!
Solution: Add another layer of inheritance. This solution aims to provide a common interface for all concrete enemy types while maintaining the desired behaviour of the Visitor Pattern.
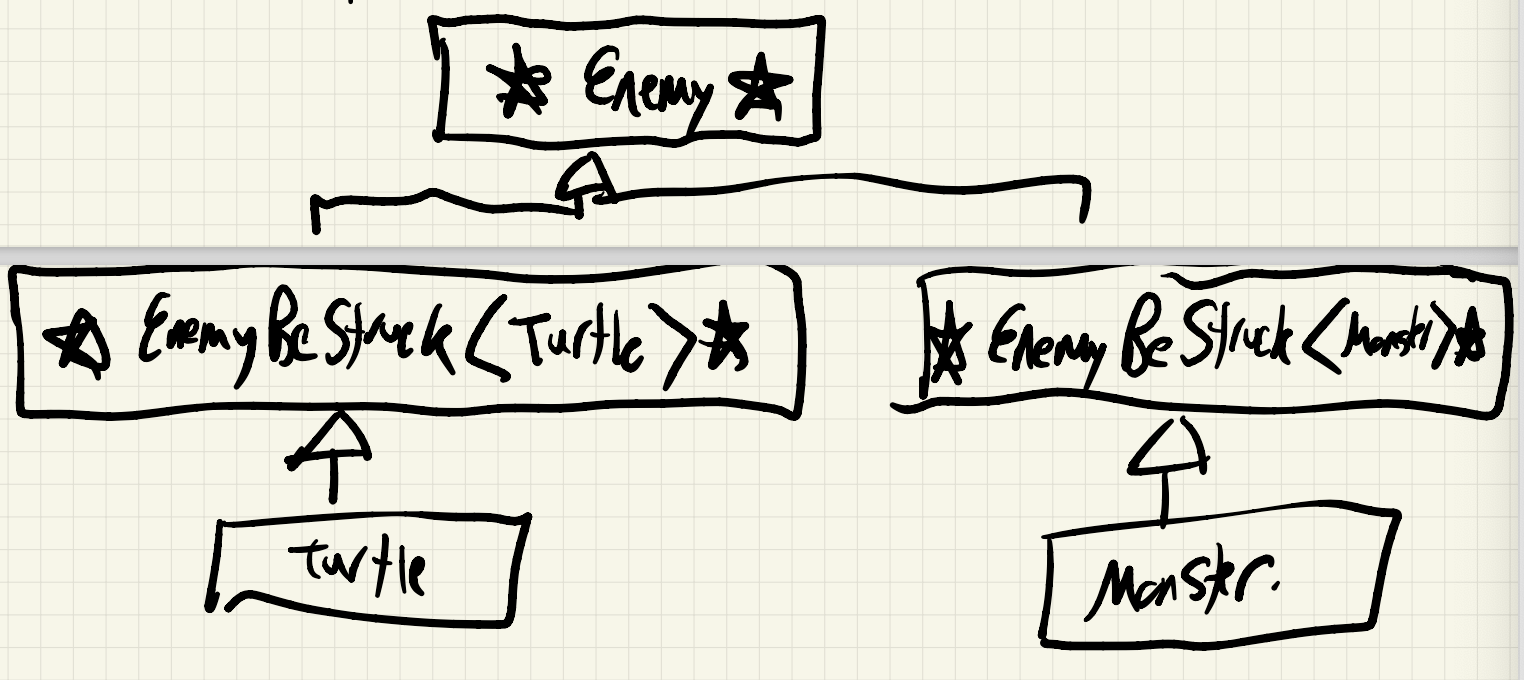
class Enemy{
public:
virtual void beStruckBy(Weapon& w) = 0; // abstract class with pure virtual function defined
virtual ~Enemy() {}
};
template<typename T> class EnemyBeStruck: public Enemy { // abstract class
public:
void beStruckBy(Weapon& w) override {
w.strike(*static_cast<T*>(this)); // converts this to a turtle or monster
}
virtual ~EnemyBeStruck() = 0; // need to implement that
};
template<typename T> EnemyBeStruck<T>::~EnemyBeStruck<T>(){}
class Turtle: public EnemyBeStruck<Turtle> {...}
class Monster: public EnemyBeStruck<Monster> {...}- The
Enemyclass defines a pure virtual functionbeStruckBy, creating a common interface for all enemies. - The
EnemyBeStruck<T>class inherits publicly fromEnemyand implements the virtualbeStruckByfunction by using CRTP. It also provides a virtual destructor, which should be defined outside the class as you’ve shown. - The concrete enemy classes (
TurtleandMonster) specialize theEnemyBeStrucktemplate class by providing the derived type (TurtleorMonster) as the template argument. This allows them to inherit the behaviour ofEnemyBeStruckand provide their own specific implementations.
Now we have a public interface by which all our concrete enemies follow: they can all beStruckBy weapons.
We use this virtual method in Enemy to resolve beStruckBy to either EnemyBeStruck<Turtle> or EnemyBeStruck<Monster> (when we have a pointer to Enemy)
Then just static_cast to T* - and we’re good.
Weapon* w = ...;
Enemy* e = new Turtle{...} / new Monster{...};
e->beStruckBy(*w);Another problem CRTP can solve: Polymorphic cloning
Recall abstract book hierarchy:
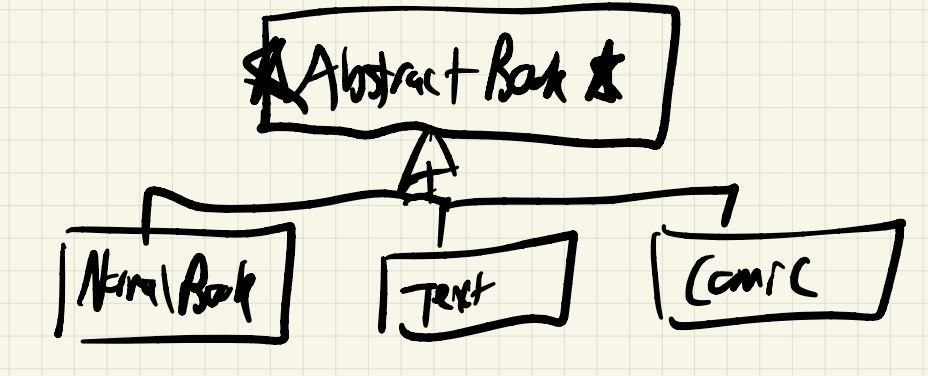
Say I have:
AbstractBook* b = ...;I want a deep copy of whatever b points to. I cannot just do this:
AbstractBook* b2 = new AbstractBook{*b}This attempts to create an AbstractBook by invoking its constructor. Wrong for 2 reasons:
AbstractBookis abstract, we cannot instantiate those objects- Ignoring what we’re actually pointing at, we actually want to invoke a constructor that depends on the dynamic type of
b.
We can provide a virtual clone method for the purpose of solving this.
class AbstractBook{
public:
virtual AbstractBook* clone() = 0;
virtual ~AbstractBook() {}
};
class Text: public AbstractBook{
public:
Text* clone() override {
return new Text{title, author, length, topic};
}
};
// Similar with a Comic/Normal Book
AbstractBook* b = ...;
AbstractBook* b2 = b->clone();Instead use the copy constructor in each of our clone methods to simplify the implementation.
class Text: public AbstractBook {
public:
Text* clone() override {
return new Text{*this}; // creates a new Text based on the constant lvalue of this
}
};
// Exact same code in Normal Book and Comic just the type of this and the type of constructor which is changingOnce again, we can use CRTP.
class AbstractBook {
public:
virtual AbstractBook* clone() = 0;
virtual ~AbstractBook() {}
};
template<typename T> class BookClonable: public AbstractBook {
public:
T* clone() override {
return new T{*static_cast<T*>(this)};
}
virtual ~BookClonable() = 0; // implement this outside of class, makes this class abstract
};
template<typename T> BookClonable<T>::~BookClonable<T>() {}
class Text: public BookClonable<Text> {...}
class Comic: public BookClonable<Comic> {...}
AbstractBook* b = new Text{...} / new Comic{...};
AbstractBook* b2 = b->clone();b->clone() is virtual, so if b points at a Comic, we call BookClonable<Comic>::clone - static_cast this into a Comic* and invoke the Comic copy constructor with the Comic&.
Provided for all subclasses - reduces boilerplate code.
Command Pattern
About using objects to encapsulate behaviour of some “action” within a system.
Example: Consider writing an IDE. Using MVC - we might have Model/Control relationship where Controller calls Model methods, like :
Model::insert Text
Model::copy
Model::paste
Model::ChangeSyntaxHighlightingThis is a decent decision - but it doesn’t allow for some features we might desire:
- Macros - replaying sequences of instructions
- Undo / Redo
Command Pattern: Instead of manipulating the model directly - we pass Commands to an Invoker.
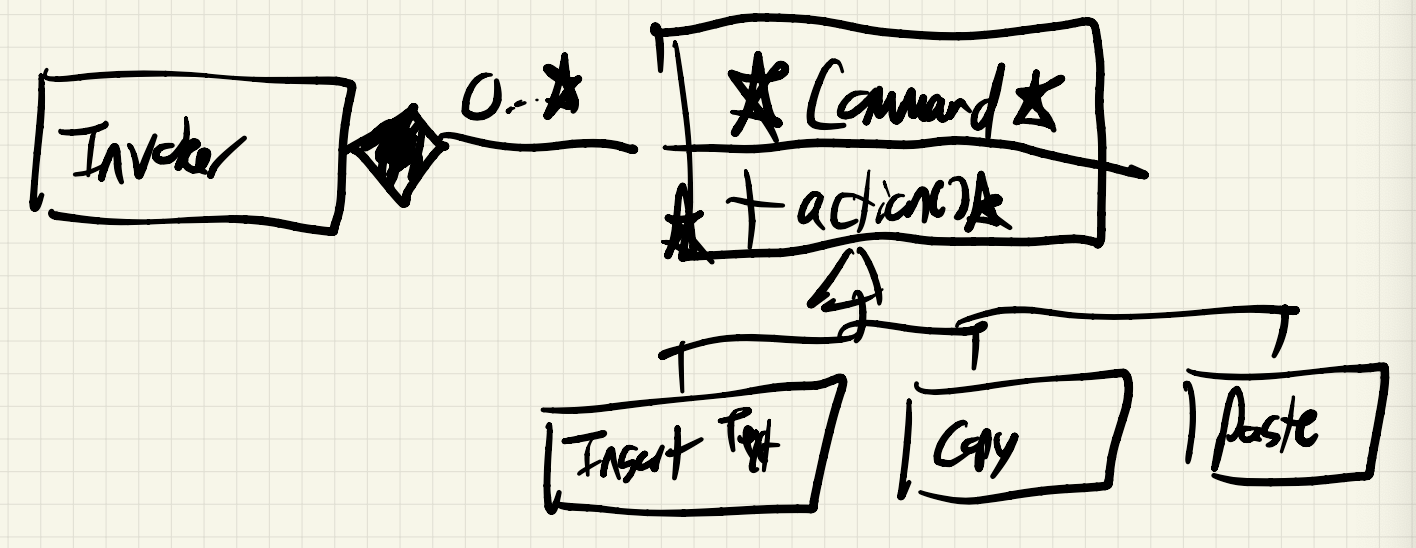
Command object has whatever information it needs to perform its given action - maybe the Model, maybe sub objects within the model
- Controller would create command objects, supply with info they need
- Sends abstract commands to the Invoker for processing
- Invoker calls each action method to execute the command.
Invoker can hold additional information!
Invoker can maintain additional state - stack of Commands for undo / redo, or mapping of a macro keyword to a list of commands.
Next: CS247 Lecture 22